UDP receiver

Implemented from firmware version 3.3.0
This job triggers any telegrams in KNX according to previously defined contents of specific UDP network packets. Thus, in conjunction with the job "UDP sender", a bidirectional connection of UDP-based applications with the EIBPORT and thus the KNX system is possible.
Job Name
Required field. Assign a unique name for the job. The name must not contain more than 15 characters.
Enable object
The enable object enables or disables the job. It is an EIS 1 object:
Group address not assigned = job enabled
Group address entered, value 1 = job enabled
Group address entered, value 0 = job is disabled
Group address entered, no value = job is disabled
As soon as an address is entered into the field, the enabling will respond according to the value of the group address. If no value has yet been sent to the address, i.e., it is without value, the job is disabled.
Port
Enter here the port number on which the desired application is to send your UDP data to the EIBPORT: 1-65535.
Protocol analysis
Packet encoding
Select the character encoding which was used to encode the incoming packet. The following is available:
ISO-8859-1: character encoding, which is used, for example, by Windows systems
UTF-8: character encoding used by other systems, e. g. Linux, MAC.
If you use the wrong character encoding, the special characters of a message will not be interpreted correctly. You can see which encoding was used by consulting the sending application.
Define hits
With this selection you define which content of the desired packet is to trigger one or several KNX telegrams. You have the following options:
via ASCII protocol analysis (1 hit):
Use an analysis tool ("UDP Packet Analysis Tool") to be able to define the desired packet content as text (ASCII). The analysis tool opens after you have pressed the "Start" button. (For description of the analysis tool see below). In this mode, you can define ONE hit. Create several jobs, if several hits are required.via binary protocol analysis (16 hits):
Use an analysis tool ("UDP Packet Analysis Tool") to be able to define the desired packet content as binary code. The analysis tool opens after you have pressed the "Start" button. (For description of the analysis tool see below). In binary mode, you can define 16 hits. Use additional jobs, if more than 16 hits are required.via manual regular expression (16 hits):
If you want to use your own regular expressions, you can use this function. The configuration mask for regular expressions is enabled when you select this function. The hits are marked with brackets ("()") and numbered from the left to the right. Up to 16 hits can be defined.
ASCII protocol analysis – UDP Packet Analysis Tool
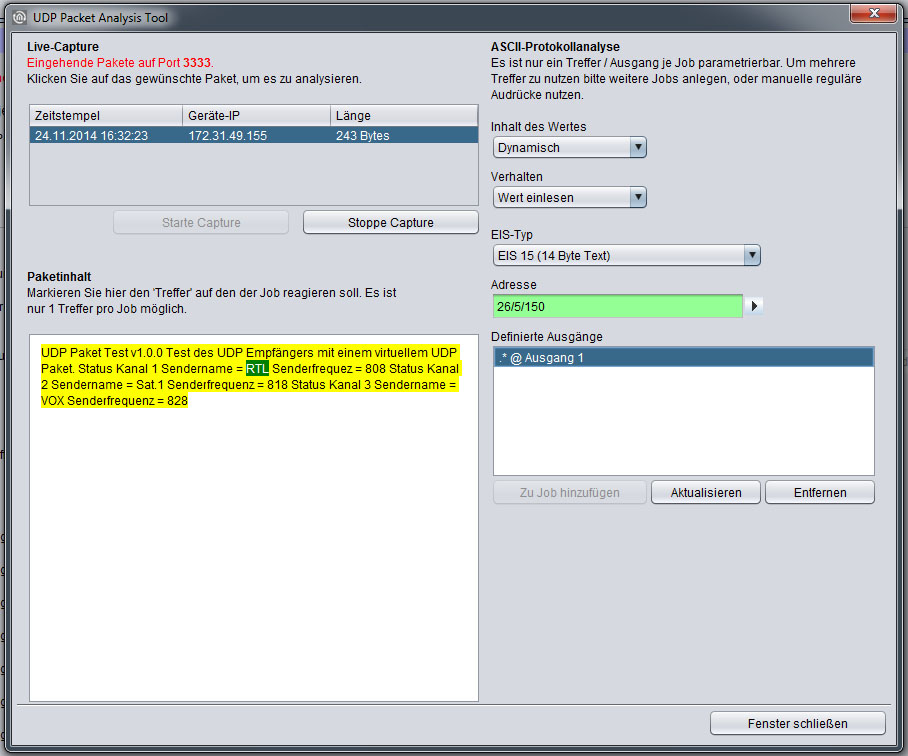
The UDP Packet Analysis Tool for ASCII protocol analysis enables you to record the datagram received, to define the desired packet content based on ASCII and to link it with a group address. The link will be automatically entered into the job mask. Only 1 hit per job is possible.
ASCII protocol analysis
Live Capture
This section lists the incoming UDP packets on the port number specified in the job mask. The specified port number is shown in red "Incoming packets on port XXXX". The buttons below this list can be used to start or stop packet recording (capture). The recording function is automatically enabled when the analysis tool is started.
Packet content
To view the content of a packet, highlight the desired packet in the Live Capture list. Then, highlight the desired packet content using the mouse cursor.
Content of the value
Define whether the highlighted content is Static or Dynamic.
Behaviour
Determine how the program is to proceed if the highlighted content is included in a UDP packet.
Read value:
The highlighted value or the value which appears instead of the highlighted value, is read and sent to the appropriate group address.Report hits:
If the highlighted value exists, a previously defined value is sent to the group address. If this option is selected, the field "Value sent on hit" appears.
EIS type
Determines the EIS type of the defined output. The following types are available:
EIS 1 = 1 bit value.
EIS 5 = 2 byte floating point value.
EIS 6 = 1 byte percentage value.
EIS 9 = 4 byte floating point value.
EIS 10u = 2 byte decimal value without sign.
EIS 11u = 4 byte decimal value without sign. Formatting: see EIS 10u
EIS 14u = 1 byte decimal value without sign.
EIS 15 = 14 byte text value (up to 14 text characters).
Address
Address field to define the group address to which the output is to send (for behaviour of the address field, see above).
Defined outputs
This section displays the previously configured outputs. The following syntax is applied:
[hit content]@[output number][hit content] An "'*" indicates that the content is dynamic (see "Content of the value"). A specific character string (e. g. "ON") indicates the static content which has been defined.
[Output number]: Indicates for which output number the hit was configured.
Example:
.*@output 1 means that dynamic content has been configured for output 1. Use the "Add to job" button to load the current output configuration into the job. Administrate the list via "Update" and "Remove".
Binary protocol analysis – UDP Packet Analysis Tool
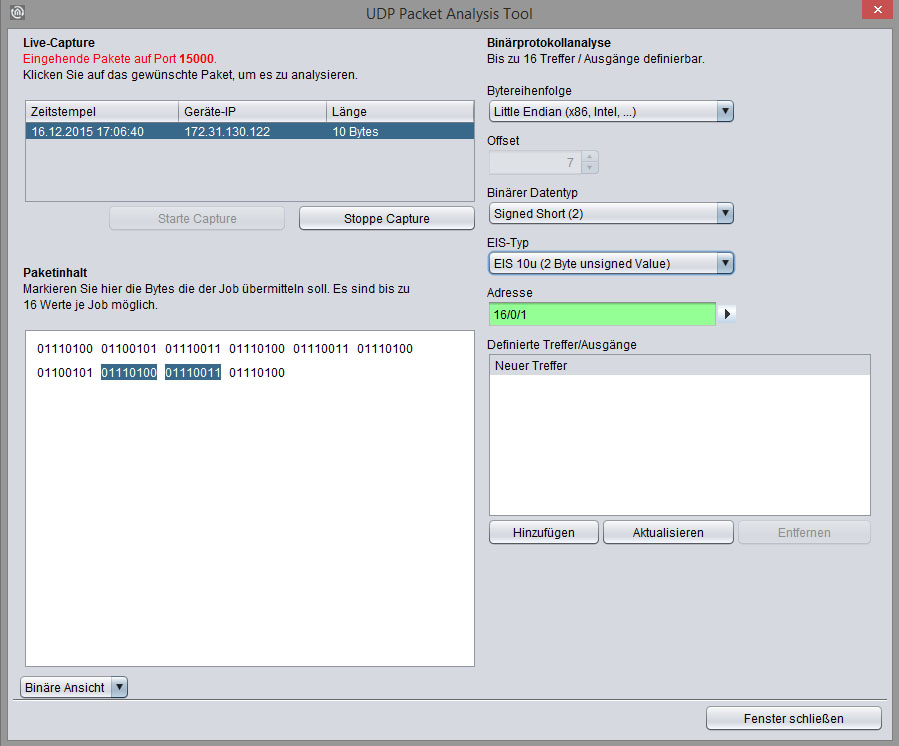
The UDP Packet Analysis Tool for binary protocol analysis enables you to record the datagram received, to define the desired packet content based on binary code and to link it with a group address. The link will be automatically loaded into the job mask. 16 hits per job are possible.
UDP receiver – Binary packet analysis
Live Capture
See "ASCII protocol analysis“.
Packet content
To view the content of a packet, highlight the desired packets in the Live Capture list. Then, highlight the desired packet content using the mouse cursor.
Endianness
The selected byte order determines how binary contents of 2 and 4 bytes are interpreted for conversion to KNX data types.
Little Endian (x86, Intel, …) = least significant byte is stored at the first location
Big Endian (ARM, Motorola, Power PC, … ) = most significant byte is stored at the first location
Offset
Display element Shows the non-highlighted bytes calculated from byte 0.
Binary data type
Depending on the bytes highlighted in the packet content, all binary data types which can be selected will be shown. It is important that the correct selection is made so that the value is correctly interpreted for further use (with / without sign, floating point number etc.)
EIS type
See “ASCII protocol analysis”.
Address
See “ASCII protocol analysis”.
Defined outputs
See "ASCII protocol analysis"
Note: When you close the "UDP Packet Analysis Tool", the packet content information will be lost. When you re-open the window, the output (hit) information will still be available but for the packet content to be shown again and for the highlighted strings to be shown again, the packet has to be re-sent.
Manual regular expression
A regular expression is used to filter the content of the packet and transmit the result to one of the outputs. A regular expression is a string of characters in which the different characters have different filter functions. Please refer to the internet, for information on the functioning of regular expressions.
Regular expression
Enter the desired expression here. In the regular expression, each "hit / output" is represented by a group. A group is within (). In addition, the following flags can be used for the filter:
Case Insensitive:
Upper-case and lower-case letters are treated as being the same.Multiline:
Must be enabled if the expression is to span several lines.Ungreedy:
Instead of looking for as many matches as possible ("greedy"), filtering stops after the first match is found.Dot All:
If enabled, the expression "." also ignores the end of lines. This is useful in connection with "multiline" and a hit over any number of lines.Extended:
Activates extended functions which enable the filtering of comments in complex texts.
Number of hits
Select here the number of hits / output fields which are to be enabled for configuration.
Hit / output #1 - #16
Define here the group address, EIS type and mode for the corresponding hit which is represented by () in the regular expression.
EIS type
See "ASCII protocol analysis"
Mode
See description on "Behaviour" under "ASCII protocol analysis"
Example
An example for a configuration with regular expressions using XML data of the openweathermap API: XML data:
<current>
<city id="2643741" name="City of London">
<coord lon="-0.09" lat="51.51"/>
<country>GB</country>
<sun rise="2015-06-30T03:46:57" set="2015-06-30T20:21:12"/>
</city>
<temperature value="72.34" min="66.2" max="79.88" unit="fahrenheit"/>
<humidity value="43" unit="%"/>
<pressure value="1020" unit="hPa"/>
<wind>
<speed value="7.78" name="Moderate breeze"/>
<direction value="140" code="SE" name="SouthEast"/>
</wind>
<clouds value="0" name="clear sky"/>
<visibility value="10000"/>
<precipitation mode="no"/>
<weather number="800" value="Sky is Clear" icon="01d"/>
<lastupdate value="2015-06-30T08:36:14"/>
</current>Regular expression used:
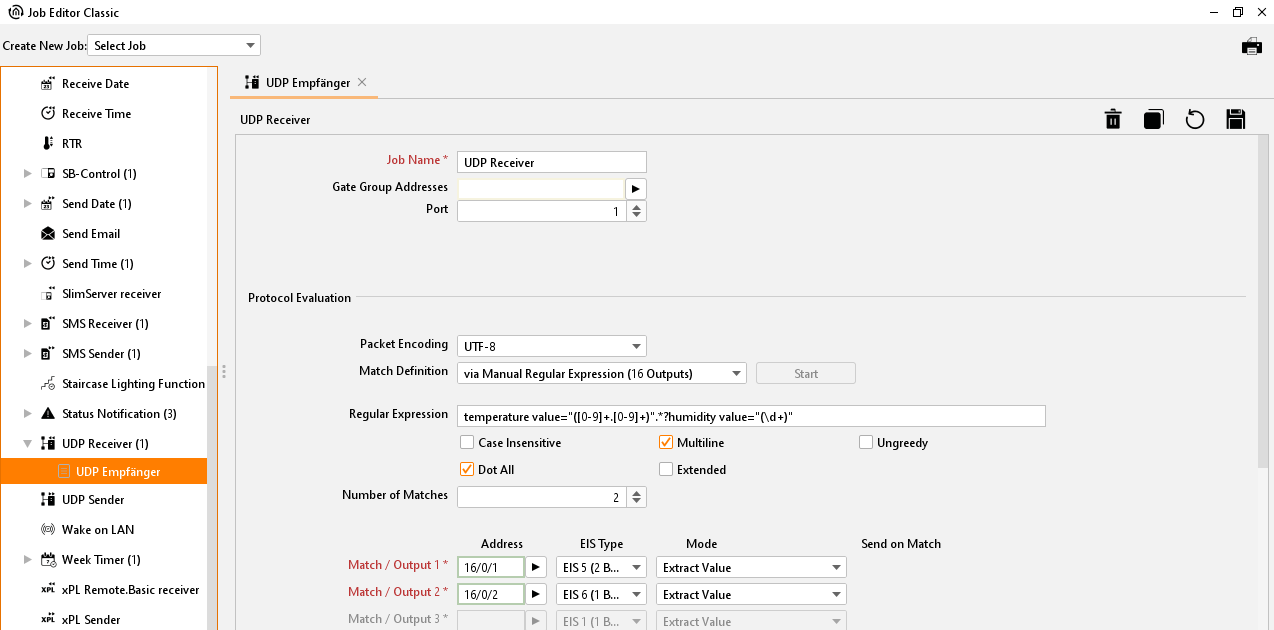
temperature value="([0-9]+.[0-9]+)".*?humidity value="(\d+)"Flags used:
Multiline
Dot All
The expression filters the values "72.34" (temperature) and "43" (humidity), thus 2 outputs are defined as follows:
Hit / output 1: EIS type = EIS 5 or EIS 9 (floating point number), mode = read value
Hit / output 2: EIS type = EIS 6 (percentage), mode = read value
UDP receiver – Example
