Counter
With the counter job eight input objects could be counted. Therefore, seven different counting operations are available. Furthermore, the job can be controlled by a gate object.
EIS formats
The counter job supports the following datatypes at th input and output objects:
EIS 1 (1 Bit)
EIS 5 (2 Byte FP)
EIS 6 (1 Byte)
EIS 9 (4 Byte FP)
EIS 10s (2 Byte Value)
EIS 11s (4 Byte Value) 1
EIS 14u (1 Byte unsigned)
EIS 15 (14Byte Text)
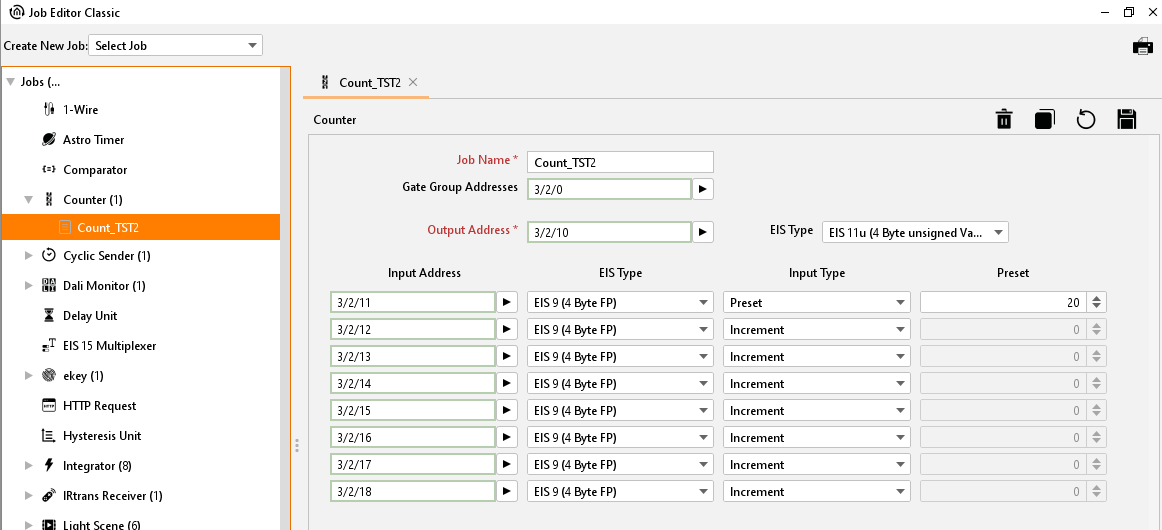
Job Editor Classic – Job mask counter
Job Name
Required field. Assign a unique name for the job. The name must not contain more than 15 characters.
Gate Group Addresses
By Gate Group Addresses job will be released or blocked. The release object releases or locks the job. It is about an EIS1 object:
Field blank = Job is released.
Field completed, value 1 = Job released.
Field completed, value 0 = job locked.
Field completed, no value = job locked.
As soon as one address is filled in, release will behave respective to the value of the group address. If no value was sent to the address and the address is presently without values, job will be blocked.
Input Type
The counter job can perform different counting operations depending on the input type which is chosen. These are:
Disabled: The input is counted.
Increment: With receiving a telegram, does not matter of which datatype and of which value, the result is counted beyond by one. The number of the incoming telegrams has been counted.
Decrement: With receiving a telegram, does not matter of which datatype or which value, the result is reduced by one. The number of the incoming telegrams has been counted.
Add Value: The value of the input telegram has been added to the present calculated value.
Sub Value: The value of the incoming telegram has been subtracted from the present calculated value.
Clear: Is an entry detected on this input the result of the counter will be set back to this value (the start value).
Preset: With this option an initial value can be used for the further calculation. With it is is possible to set a kind of offset value.
Preset Value: The value of the incoming object will also be used as the value for the output object.
Preset
The preset value can be determined if the corresponding counter operation has been chosen. Thus, causes that the value has been used by every further operation as the base. The preset value in this case forms a kind of offset value.
Important: Pay attention that the counted value is not exceeding the range of the output’s datatype.
